Calendar
Exploring Java and Angular.js creating a full calendar with angular methods and delegations
Java Spring Boot Collection
- Bookit
- fortune-ai
- happy2be
- [calendar] calendar
- lazy-image-loader
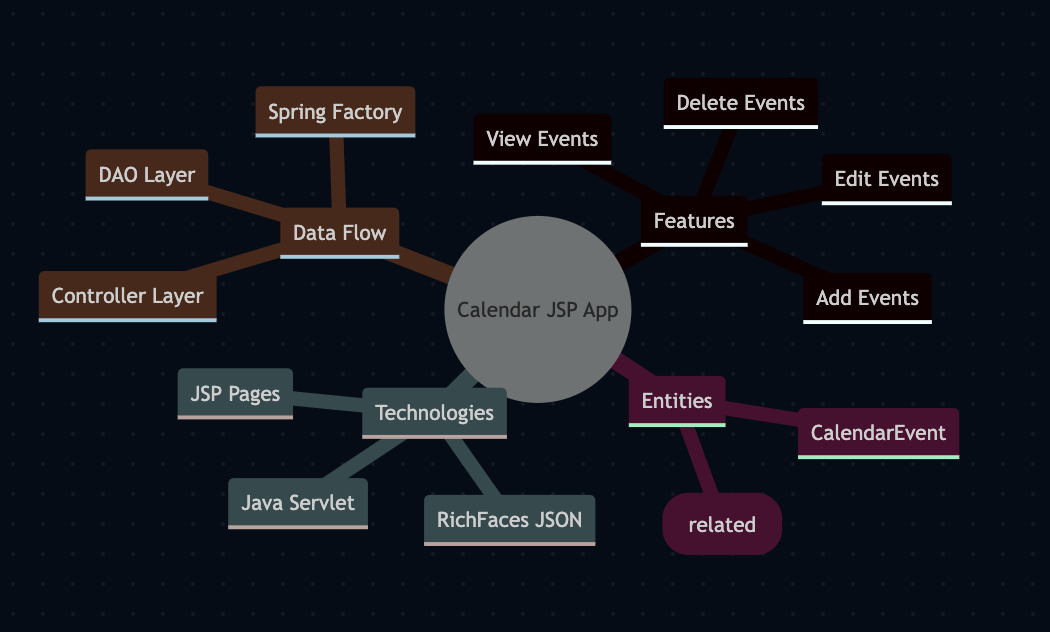
This application is an older version of the bookit application however the bookit is a rest microservice whereas this application is a full stack java implementation. Java framework coupled with a mix of Angular.js V2 framework and full calendar jsp (Jakarta Server Pages) server-side technology that enables developers to create dynamic web content. A JSP file typically has a .jsp extension and combines static content, such as HTML or XML, with dynamic elements written in Java.
Visit the repo and kick start your project!
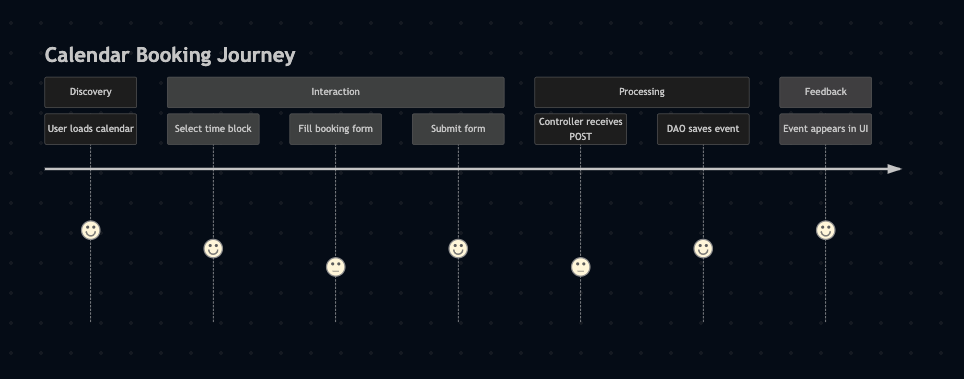
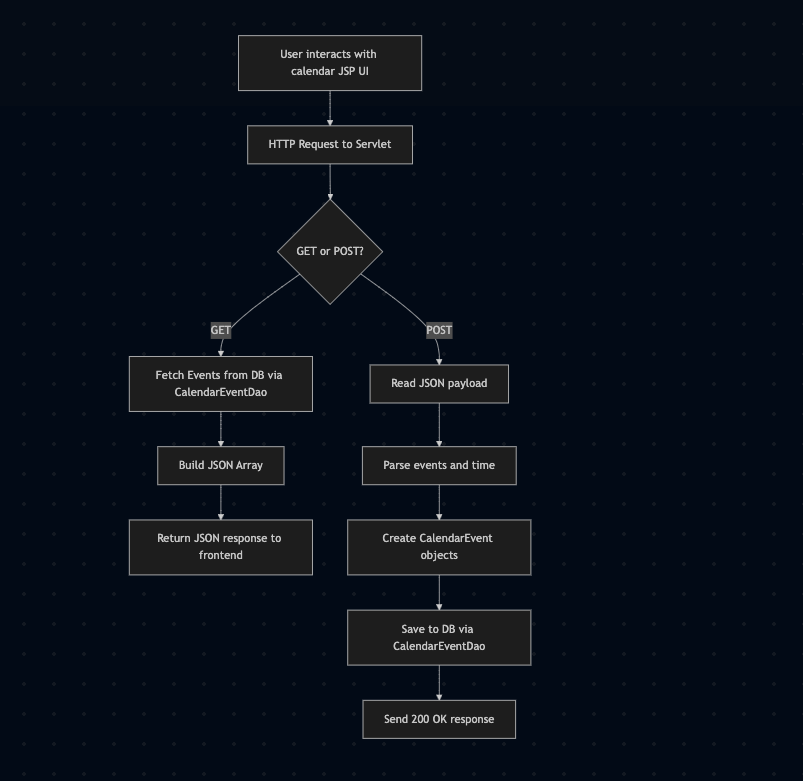

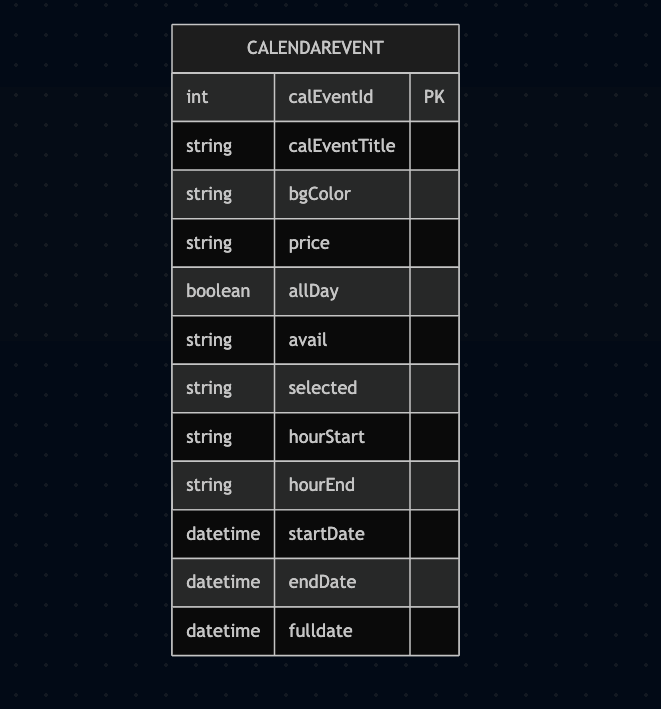
A snippet of the Calendar Event Dao below of the data flow to the database connetivity useing hibernate Query and session states.
import entity.CalendarEvent;
public class CalendarEventDao extends HibernateDaoSupport {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public List<CalendarEvent> getCalendarEvents(){
return getHibernateTemplate().loadAll(CalendarEvent.class);
}
public CalendarEvent getCalendarEventByCalendarEventId(int cEventId) {
return (CalendarEvent) getHibernateTemplate().get(CalendarEvent.class, cEventId);
}
public void addCalendarEvent(CalendarEvent cEvent) {
getHibernateTemplate().save(cEvent);
}
public Long getRowCount() {
Session dbSession = getSession();
Query dbQuery= dbSession.createQuery(
"select count(calEventId) from entity.CalendarEvent");
Long count = (Long) dbQuery.uniqueResult();
dbSession.close();
return count;
}
}
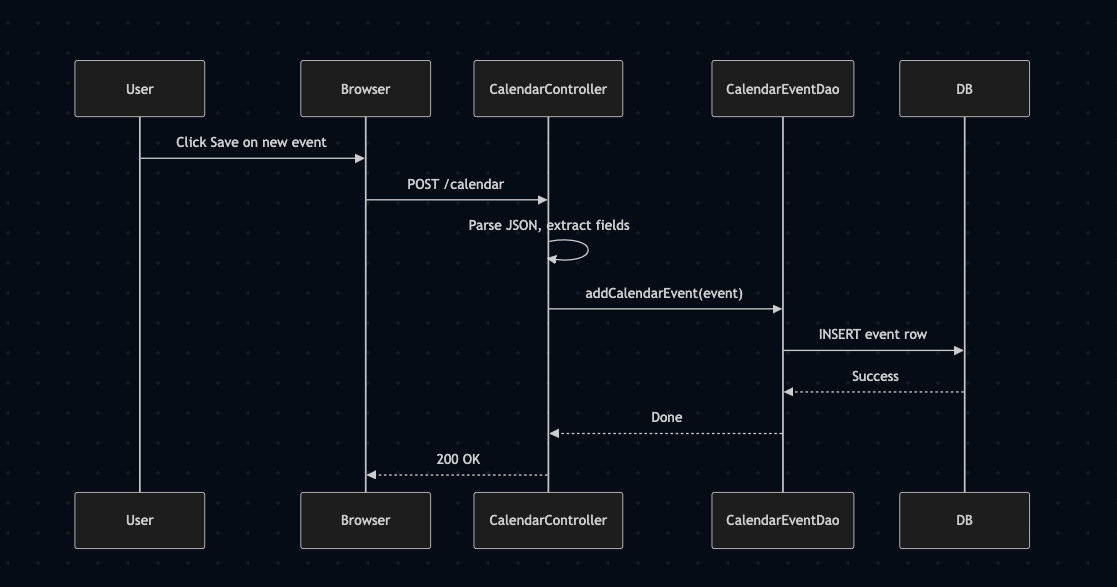
Explanation – Saving an Event (Sequence Diagram)
When a user interacts with the calendar interface to add a new event, the following sequence of actions occurs:
User Action: The user clicks a “Save” or similar button after entering event details on the calendar interface.
Browser Request: This triggers a POST request to the server, specifically targeting the CalendarEventController.
Controller Processing:
The controller receives the JSON payload. It parses the incoming data to extract event fields (such as title, time, colors, and availability). It creates a CalendarEvent object using these values.
Data Persistence:
The controller calls the CalendarEventDao.addCalendarEvent() method. The DAO constructs a database query (likely an INSERT) and sends it to the database.
Database Response:
The database executes the query and returns success (or failure). The DAO confirms completion back to the controller.
Final Response:
The controller sends back a 200 OK HTTP response to the browser. The event is now considered saved, and the front-end can refresh or update the calendar display to show the new booking.

Testing example
Lets run some testing of the calendar using assertions to test the calenar event functions.
@Test
public void testAddCalendarEvent() {
final CalendarEvent event= new CalendarEvent();
event.setCalEventTitle("Apothecary");
event.setBgColor("#cde9b5");
transactionTemplate.execute(new TransactionCallbackWithoutResult() {
protected void doInTransactionWithoutResult(TransactionStatus status) {
calendarEventDao.addCalendarEvent(event);
assertTrue( event.getCalEventId() > 0 );
CalendarEvent event4 = calendarEventDao.getCalendarEventByCalendarEventId( event.getCalEventId());
assertEquals( event.getCalEventTitle(), event4.getCalEventTitle());
assertEquals( event.getBgColor(), event4.getBgColor());
status.setRollbackOnly();
}
});
}